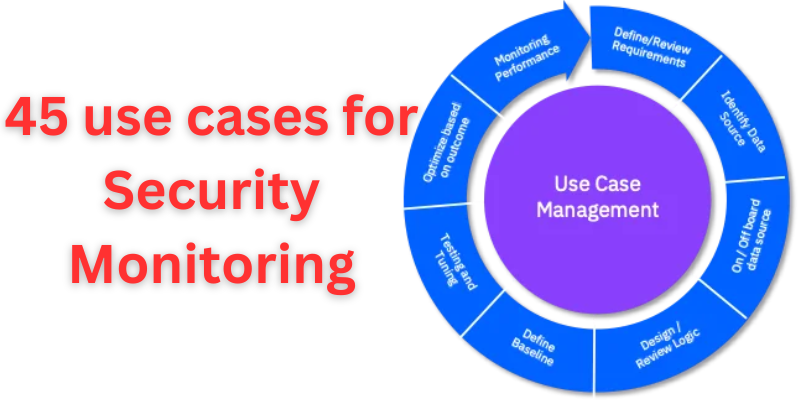
What is SIEM Usecases
SIEM, which stands for Security Information and Event Management, encompasses a wide range of use cases within cybersecurity. It involves collecting, analyzing, and correlating security data from various sources across an organization’s network infrastructure. Some common SIEM use cases include threat detection, incident response, compliance management, user activity monitoring, and network visibility. These use cases aim to strengthen security measures, identify potential threats or anomalies, facilitate timely responses to security incidents, and ensure adherence to regulatory requirements.
What are the SIEM Top Usecases for Boosting Cybersecurity Defenses?
DMZ Jump
This rule will be triggered when connections appear to be joined across the network’s DMZ.
DMZ Reverse Tunnel
This rule will be triggered when connections appear to be joined across the network’s DMZ via a reverse tunnel.
Excessive database connections
The rule detects an excessive number of successful connections to the database.
Firewall overload accepts on multiple hosts
Reports excessive firewall acceptances on multiple hosts. More than 100 events were detected on at least 100 unique destination IP addresses in 5 minutes.
Overhead firewall accepts from multiple sources to a single destination
Reports excessive Firewall Accepts the same destination from at least 100 unique source IP addresses in 5 minutes.
Excessive firewall denies single source
Reports excessive firewall rejections from a single host. Detects over 400 firewall denial attempts from a single source to a single destination in 5 minutes.
Long running flow involving a remote host
Reports a communication flow to or from the Internet with a sustained duration of more than 48 hours. This is not typical behavior for most.
Applications. We recommend that you investigate the host for possible malware infections.
Long-lived ICMP flows
Detection of long-lasting ICMP packets between hosts. This is rare and should never happen.
Outbound connection to a foreign country
Reports successful logins or access from an IP address known to be in a country that does not have remote access rights. Before enabling this rule, we recommend that you configure the active list: Countries without remote access building block.
Potential Honeypot Access
Reports an event directed to or coming from an address defined by a honeypot or tarpit. Before enabling this rule, you must configure the Activelist: Honeypot-like addresses building block and create the appropriate sentinel from the network monitoring interface.
Remote access from a foreign country
Reports successful logins or access from an IP address known to be in a country that does not have remote access rights. Before enabling this rule, we recommend that you configure the Activelist: Countries without remote access building block.
Remote incoming communication from a foreign country
Reports traffic from an IP address known to be in a country that does not have remote access rights. Before enabling this rule, we recommend that you configure the Activelist: Countries without remote access building block. SMTP and DNS were removed from this test as you have little control over that activity. You may also need to remove web servers in the DMZ that are often scanned by remote hosts with web scanners
Single IP with multiple MAC addresses
This rule will be triggered when the MAC address of a single IP changes multiple times over a period of time.
Systems that use many different protocols.
Local system that connects to the Internet on more than 50 DST ports in one hour. The connections must be successful. This rule can be edited to also detect failed communications, which can also be useful.
Authentication: Login errors followed by success on the same destination IP
Reports multiple login failures on a single host, followed by a successful login to the host.
Authentication: Login errors followed by success on the same source IP
Reports multiple login failures on a single host, followed by a successful login to the host.
Authentication: Login errors followed by success with the same username
Reports multiple login errors followed by a successful login from the same user.
Authentication: Login to a disabled account failed
Reports a host login message from a disabled user account. If the user is no longer a member of the organization, we recommend that you investigate any other authentication messages received from the same user.
Authentication: Expired account login failed
Reports a host login error message for a known expired user account. If the user is no longer a member of the organization, we recommend that you investigate any other authentication messages received.
Authentication: Successful login after scan attempt
Reports a successful login to a host after network handshake has been performed.
Authentication: Multiple login errors for a single username
Report authentication failures for the same username.
Authentication: Multiple login errors from the same source
Report authentication failures in the same source IP address more than three times, on more than three destination IP addresses in 10 minutes.
Authentication: Multiple login errors to the same destination
Reports authentication failures on the same destination IP address more than ten times, from more than 10 source IP addresses in 10 minutes.
Authentication: Multiple VoIP login errors
Report multiple login errors on a VoIP PBX.
Authentication: No activity for 60 days
This account has not been logged in for more than 60 days.
Authentication: possible shared accounts
Detection of ShaRed beads. You will need to add additional system accounts with false positives and NO when the event username matches the following
Authentication – Repeating non-Windows login errors
Reports when a source IP address causes an authentication failure event at least 7 times on a single destination within 5 minutes.
Authentication: Repeat Windows login errors
Reports when a source IP address causes an authentication failure event at least 9 times on a single Windows host in 1 minute.
VPN Sneak Attack
Check where remote users connect from and what they access. Access to a VPN connection can be misused to gain access to the intranet.
Unpatched failing ports, services, and hosts or network devices
Unusual traffic is identified as a possible intrusion; There are no signatures involved in the process, so it is more likely to detect new attacks for which signatures have not yet been developed.
Brute force attack
Check for attempts to gain access to a system by using multiple accounts with multiple passwords.
Privileged user abuse
Monitor for misuse of privileged user access, such as root or administrator access, to conduct malicious activities.
Advanced use cases What are the SIEM Top Usecases for Boosting Cybersecurity Defenses?
1.Unauthorized access to the application
1.What systems have suspicious application access/activity?
2.Are canceled accounts still being used?
3.What accounts are used from suspicious locations?
4.Access monitoring of high-risk users
5.Privileged user monitoring
2.Worm/Malware Propagation Monitoring
1.Malware Beacon Monitoring
2.CNC access monitoring
3.CNC completion monitoring
4.Malware/Worm Propagation Monitoring
5.Antivirus status/infection trends
3.Hacker Detection
1.Who attacks me and where do they attack me from?
2.Which of my internal systems are being attacked?
4.VPN Sneak Attack
5. Unpatched failing ports, services, and network hosts/devices
6.Brute force attack
7.Abuse of privileged users
Read About NAT